WIM has been employed as a major technology to collect heavy vehicles’ data on the freeways. Because WIM is one of the most costly and sophisticated data collection system, how to effectively utilize the valuable WIM data, monitor WIM stations’ performance, and identify out of calibration stations are especially important. In this project, CLR proposed an innovative and yet practical approach to develop an Inductive Loop Signature-WIM based real-time heavy vehicle monitoring system that combines the use of both WIM data and the inductive loop signature data. The integration of inductive loop signature technology offers a low-cost solution to monitor the performance of the WIM stations, identify out-of-calibration stations, and provide ground-truth truck movement data to be used for calibration. Therefore the development of the Inductive Loop Signature-WIM based Heavy Vehicle Monitoring System will not only reduce the cost of WIM calibration, but also provide the ability to monitor system performance continuously.
In Phase I project, we demonstrated the proof of concept of the proposed approach in the real world and investigated its potential applications, such as the estimation of truck activities and loading distributions and the calibration of WIM stations. With the implementation of the proposed system, the potential benefits to the national transportation system are as follows:
In Phase II, we will aim to develop a prototype Commercial Vehicle Tracking System (CVTS) to track vehicles across WIM, CCS, and CVC stations in a freeway network and then demonstrate its performance through above-mentioned applications. The system will utilize the existing WIM stations to obtain WIM data and loop infrastructure widely deployed in the field to generate high-resolution vehicle signatures for commercial vehicle classification and tracking. Non-commercial vehicles can potentially be tracked and classified as well. We will focus on developing the core algorithms, enhancing the prototype system, and expanding its capabilities to multiple stations and various applications.
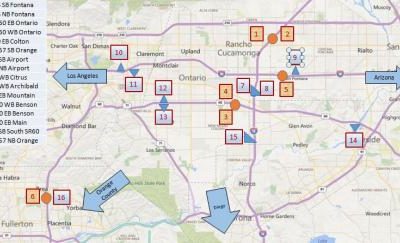
The study site for Phase II is as shown in the figure above. The site is located in Orange, Riverside and San Bernardino area. Caltrans District 8 and 12 provide strong supports on this project.
With the goal to make the proposed technology transferrable to the practice, the objectives of Phase II are listed as follows:
Sponsor: USDOT/RITA/Volpe Center
Project Time Period: October 2012 – October 2013 (Phase I)
Project Time Period: October 2014 – October 2016 (Phase II)