This software review compares two microscopic vehicle simulation packages that are commonly used by transportation professionals; Paramics (version 6.8.0) and Vissim (version 5.3-00). Paramics is developed by Quadstone Paramics Ltd, a Scottish company under Pitney Bowes Business Insight, and Vissim is developed by Planung Transport Verkehr (PTV), a German based company. Paramics and VISSIM both aim to accurately simulate vehicular traffic while presenting a friendly and intuitive user interface.

In order to make Paramics (e.g., 6.9.3) work under the latest Windows 8 and 10 computers, users will need to install the latest driver for its USB dongle since the driver coming with Paramics 6.9.3 installer only supports Windows 7 or lower. The owner of USB dongle was SafeNET and Gemalto is the current owner.
The website to download the driver is as follows and the right one to choose is the first one, Sentinel HASP LDK – Windows GUI Run-time Installer.
You may want to uninstall Paramics and then install a new version. However, after uninstalling Paramics from your computer, you may get a message saying you can’t install Paramics because it has been installed. This problem occurs when full administrative permissions are not available when the software is uninstalled. What you can do are as follows:
The current version of Paramics 6.8.0 (July 2011 and Sep 2011 versions) has a lanechoices bug if you associate destination zones in a lanechoice rule. When you editing the rule through GUI, you may want to choose zones 1-4. However, the data in the GUI are not translated correctly. V6.8 will understand it as zones 0-3. You may get error message “Zone 0 not in lookup table”. The workaround is to edit the lanechoices.xml file directly or select zones 2-5 for the previous case.
Evaluation of Incorporating Hybrid Vehicle Use of HOV Lanes
The objective of this study is to evaluate the impacts of allowing single-occupant hybrid vehicles into HOV lanes. In this study, a microscopic simulation method isintroduced to investigate California’s proposed hybrid-HOV policy. A microscopic simulation approach is appropriate since it is designed to model the movement and behavior of individual vehicles on urban and highway road networks. The study site is Orange County (OC) freeway network, which includes all the major freeways in Orange County except toll roads, such as I-5, I-405, SR-55, SR-22, SR-57, and SR-91.
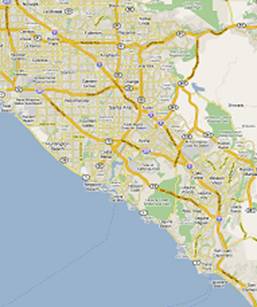
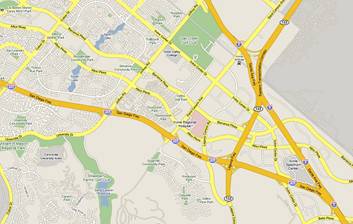
Development and Evaluation of Adaptive Ramp Metering
Several adaptive ramp metering algorithms including ALINEA, BOTTLENECK, and ZONE were developed as Paramics pluigns and they were evaluated in the enhanced Paramics environment.
Development of Hardware-in-the-Loop (HiL) Simulation and Paramics / VS-PLUS Integration
In this project, we developed a hardware-in-the-loop traffic simulation tool using Paramics. Econolite AS2 controller and a controller interface device were
used in this development. This project was conducted at University of Minnesota – Twin Cities, as sub-award from California PATH Program, UC-Berkeley.
High Priority Chokepoint Evaluation
Considering the limitations in using conventional static modeling approach, Paramics simulation model was used as an evaluation tool for cost-benefit analysis for 12 chokepoint improvement projects proposed by Caltrans District 12.
Evaluation of Automated Work Zone Information Systems (AWIS)
A Paramics simulation model for a 6-mile I-5 freeway (with a one-lane drop work zone) and its parallel street in the LA county was developed. It was used toinvestigate benefits obtained from the deployment of an AWIS system.
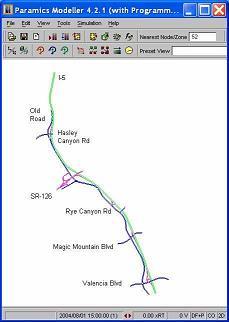

Evaluation of Incorporating Hybrid Vehicle Use of HOV Lanes
The objective of this study is to evaluate the impacts of allowing single-occupant hybrid vehicles into HOV lanes. In this study, a microscopic simulation method isintroduced to investigate California’s proposed hybrid-HOV policy. A microscopic simulation approach is appropriate since it is designed to model the movement and behavior of individual vehicles on urban and highway road networks. The study site is Orange County (OC) freeway network, which includes all the major freeways in Orange County except toll roads, such as I-5, I-405, SR-55, SR-22, SR-57, and SR-91.
Corridor Management Demonstration
This project aims to develop a template for corridor system management plans that can be used for both planning and operational analysis. The primary objective of Corridor Management Demonstration project is to improve traditional corridor management planning by incorporating detailed, multi-modal performance measurement and evaluation, and innovative micro-simulation modeling techniques. The template will help to address the problem of lost system productivity during congestion; it will also help to create effective corridor management plans, thus improving statewide transportation mobility, safety and productivity.
Development of Traffic Management Center (TMC) Simulator & Operator Training
Using the latest generation of microscopic simulation modeling techniques, a TMC operator training system has been developed and setup at California ATMS Testbed located at University of California, Irvine. The system provides an effective mechanism for the transfer of research and technology to practical uses. Three training classes for California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) operators have been conducted since the prototype system was completed in November 2005. Both Caltrans and their “student operators” are highly satisfied with the results from the training classes.
In collaboration with Beihang University of China, CLR Analytics orgnaized a Microscopic Traffic Simulation and its Applications Workshop, in Beijing, China. This workshop summarized major applications of micro-simulation and introduced details of some applications and research. The presenters of the workshop include Dr. Henry Liu from University of Minnesota, Dr. Lianyu Chu, Jeff Ban, and Dr. Meng Li from University of California Berkeley.
Place: Beihang University, Beijing, China
Time: Oct 13, 2007